M2
There are 3 different stages when producing a radio programme:
- Pre-production
- Production
- Post-production
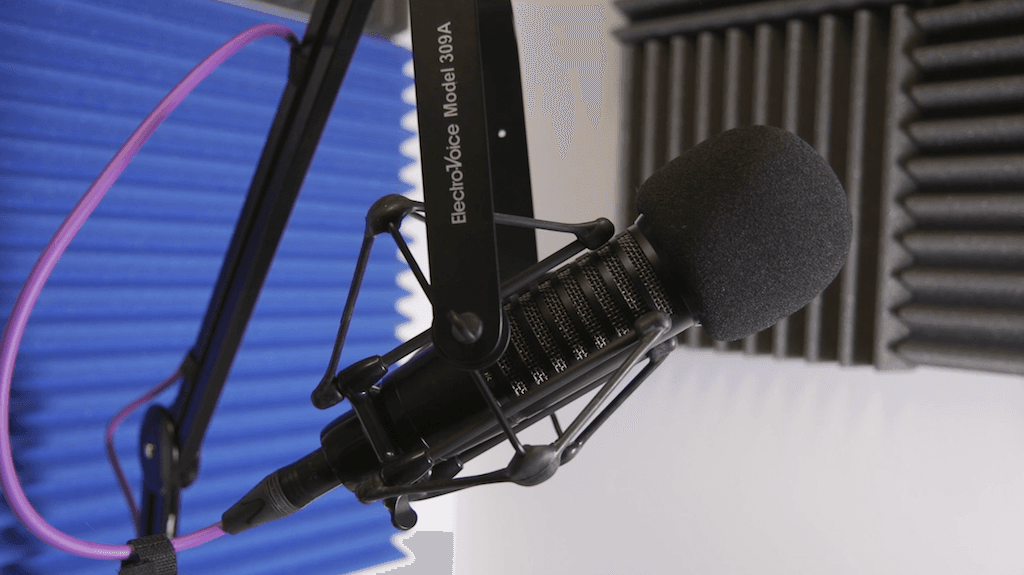
- Microphones - These are used to record the audio.
- Headphones - Producers and hosts are able to listen to the music whilst it is playing and can also hear the other members of the show (e.g. guests and co-hosts).

- Speakers - These can be used to play the audio out to multiple people.

- Workstation - This is the general workspace, including the computer used and the different software used during production and pre-production.

- Mixing desk - A piece of equipment that can adjust the audio levels and dynamics of each audio asset used in the radio show.
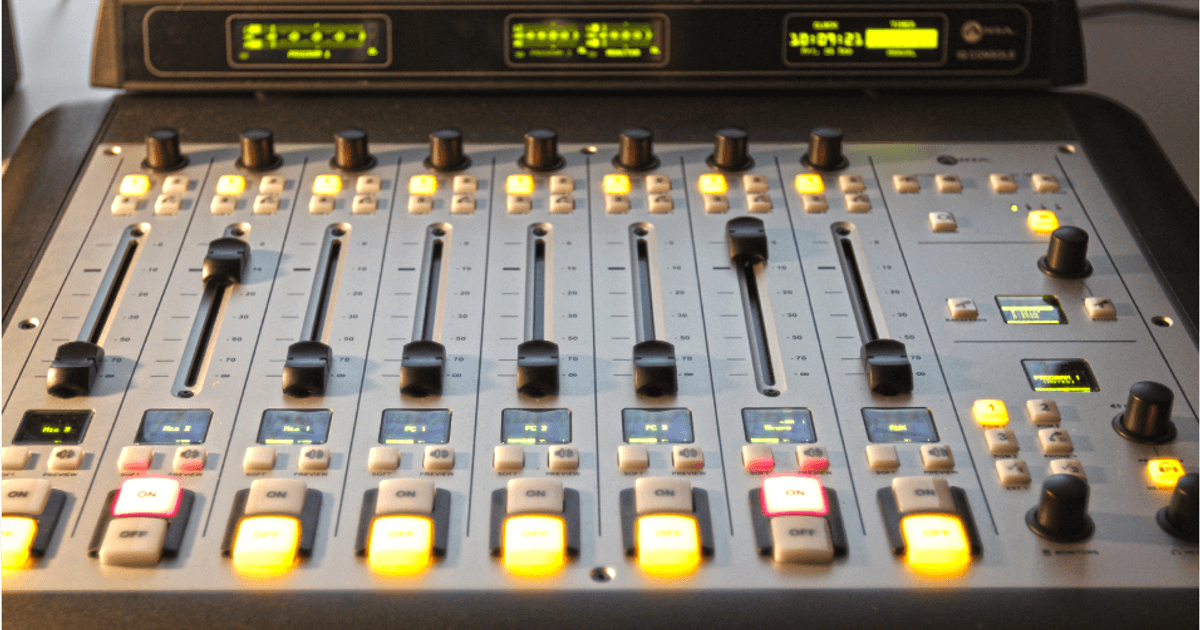

Example of Equipment Use in Radio
Previously, I have looked at BBC Radio 1 as an example of a radio station. More specifically, I looked at the Chillout Anthems show that aired between 6am-7am. Throughout this radio show, they will have used the professional recording equipment.
This show is an hour of music with no talking, therefore is most likely to be pre-recorded. This means that the post-production process will happen after the production process. In the pre-production process, the jingles will have been created in order for them to be easily inserted into the programme. As well as this, a playlist will have been put together with all of the music that will be played within the hour.
When producing the show, the producer will have used headphones to listen to the show in order to recognize any imperfections throughout the recording. These can then be adjusted using the mixing board. During this show, the songs tend to transition into each other. This effect will have been made using the mixing board, where the dynamics/volumes of each track will have been adjusted in order to make a seamless transition.
As this show is just an hour of music, there will have been no need for it to be live as it is easier for it to be a pre-recorded music show.
For my own radio show, it will be live, which is different to the programme that I have analyzed. This will be because I intend for the show to have a call in section, which will realistically make more sense to be done live. The show being live will also encourage listeners to interact during the programme and call in themselves. I will follow the principals of a live radio show by creating the jingles and necessary assets
Comments
Post a Comment